Cable User Guides
This section is meant to help users with finding cables, understanding various pinouts, and how to make your own cables from stock you may already have. Once a cable is made for sale and included in various kits, we will show all the relevant specifications (pinouts, BOM, length, etc) on the main datasheets page here
Table of contents
Comprehensive ModalAI Cable Spreadsheet and Examples
The spreadsheet file linked Here (Native Microsoft Excel format) is provided as a convienence for all customers to help find and understand the various cables we offer. It even includes information on cables that are EOL/Obsoleted, and cables in-the-works to hopefully give you a jump start.
Latest Spreadsheet Update: V3 on 5/23/23
- File updates (compared to V2):
- Added weight column (will continue to update and fill in older products)
- Added many new cables since MCBL-00075, plus several new “dash” numbers to existing cable products for length variations.
Don’t have MS Excel? We have verified the key “data filter” function works on the following two programs:
- Linux/Mac user: “OfficeOnly-DekstopEditors”
- Windows user: “Trio Office: Docs & Sheets Software”
Below are some examples how to use this file, most of which is by using the filter pull-down arrows on the top/header row.
Simple Usage: use the top row to sort and filter by the following attributes: 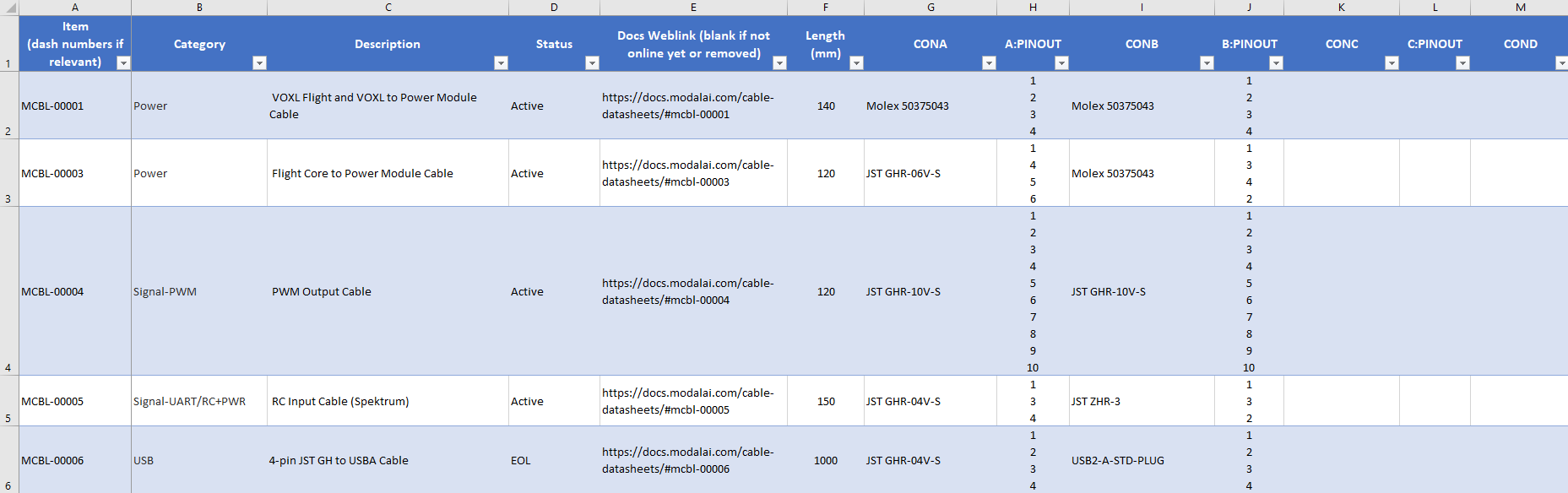
- ModalAI Item/Part Number (Default sorting order provided in the file)
- Cable Category/Type (signal, Power, USB, etc)
- Description
- Status (Active, EOL, In Development, Obsolete)
- Length (in mm): Note: Length refers to the cable conductor length measured from end-to-end, excluding any plastic shroud dimensions. This may not be provided for cables with three or more connectors if it not useful, in which case, please refer to the drawings)
- CONA (connector A manufacturer and MPN)
- CONB (connector B manufacturer and MPN)
- CONC/COND (if applicable)
NOTE: There is no convention for CONA vs CONB always being a specific type or function, so when searching for specific connector MPNs, be sure to include both ends in the A and B columns (example shown below).
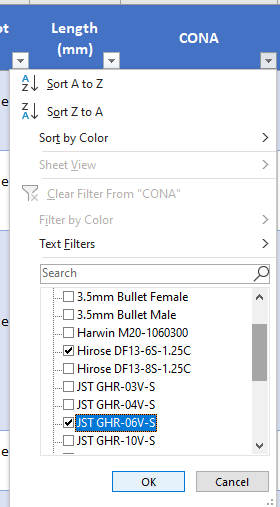
User Example 1: Find a cable by Connector Mates
Let’s say you want to find a cable that adapts a Hirose DF13-6S to a JST GHR-06. To find those relevant cables, start by clicking on the down arrow in the “CONA” column, de-select all items, and just select the “Hirose DF13-6S-1.25C” box and the “JST GHR-06V-S” box as shown here:
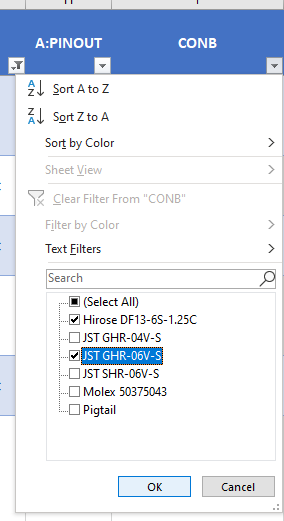
Next, repeat that same step on the CONB filter arrow (note there are now already less options to deselect) as shown here:
After this, you’ll notice the entire file has been filtered to just about six cable options showing all cables that mate DF13-6 to JST GH-6 (and JST to JST along with DF13 to DF13), as shown:
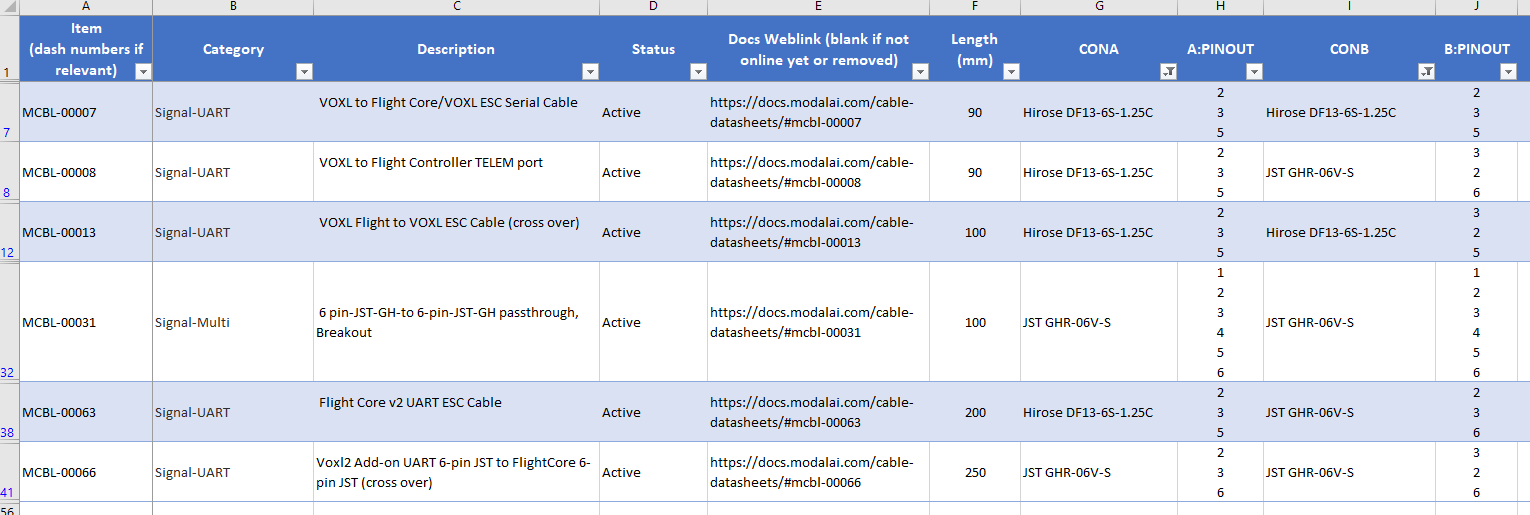
Now, with this info, you can follow the web-links provided to bring you to the TechDocs section of our website that will provide you with further information, including drawings to confirm if these work for you. If you need to validate the pinouts, see the next example:
User Example 2: Determining the Pinouts Portrayed in the file
Once you think you found a cable that meets your length, connector, or function type, the pinouts are the next important function to confirm. The pinouts are listed in this file in a sentence-line aligned format. That is, the order (from top to bottom) the pin numbers are listed in the cell matter. The image below shows some of the more complex pin assignments to see how this works:
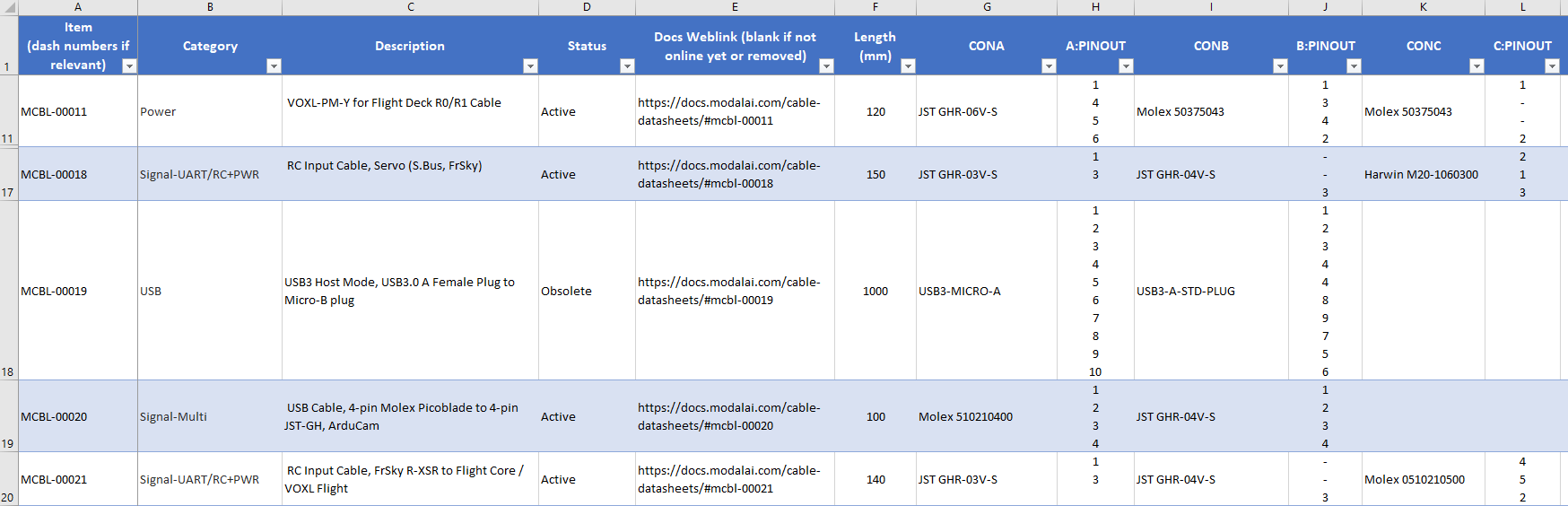
Start on the MCBL-00020, and note that the A:PINOUT and B:PINOUT show “1,2,3,4” and “1,2,3,4” respectively. This means that this is a 1:1 cable, so that pin1 of CONA connects to pin1 of CONB, and so on.
Now, look at the MCBL-00011, and note that the A:PINOUT and B:PINOUT have 4 items, with mapping 1-1, 4-3, 5-4, and 6-2. Also note there is a CONC in this assembly. On that entry for C:PINOUT we see 1, -, -, 2. What this means is that pin1 connects to pin1 of BOTH CONA and CONB, but pin2 of CONC connects to pin6 of CONA, and pin2 of CONB. Note the “dashes”. This shows that nothing on CONC connects to CONA/CONB pins 4-3, and the 5-4 connections.
Another example is on MCBL-00021, where you can see that pin1 of CONA does NOT connect to CONB, but connects to pin4 of CONC, and pin3 of CONB connects to pin2 of CONC, and there are no connections between CONA and CONB.
It can be a little bit of an eye strain at first, but once you follow through a few examples, this becomes easy and natural. And, of course, please contact us on the Forum and we will help you if you have any questions!
We take pride in providing all the information needed to propel your projects to success. We will update this file very frequently in the up-coming months, so check back often and look for the version/date codes so you can see if there are any updates. For now, there will not be a “change log” as it is a simple spreadsheet file maintained manually, so for updates, you may need to run your own diff utility if it is not obvious.
FlightCore V2 Conversion Cables Info
As we update our website and tech docs with more info for FlightCore V2, we know some “power users” are comfortable making their own cable adapters. This section will help guide users that are switching from FCv1 to FCv2 make some of the basic conversion cables. We know it’s a little terse below as we focus instead on making new cable drawings to better document all these cables going foward. If you cannot follow these instructions, please post on the Forum and we will help you out!
Upgrade Path (Compatability Drawing) Primary UART Link Cable Options:
Note: Not all the cables in the images are listed here yet or on our sales pages, but will be soon! Please reach out to us on the Forum if you need immediate sales/shipping access to these planned cables, and we will accomodate you. You can also see the tips in this section below to guide making your own cables while we get everything posted.
The following image is attempting to show what cables change for the UART/ESC/TELEM links between various systems as a user upgrades from Voxl1 or FlightCore V1 to Voxl2 or FlightCore V2. Please download ESC-UART Cable Guide Here as it is easier to see the details. This does not show all the other power and accesory cables, since those are much easier to scan our site to find, and many of them do not change between generations. We know the cables and connectors on our designs are hard to keep track of, so we hope this helps!
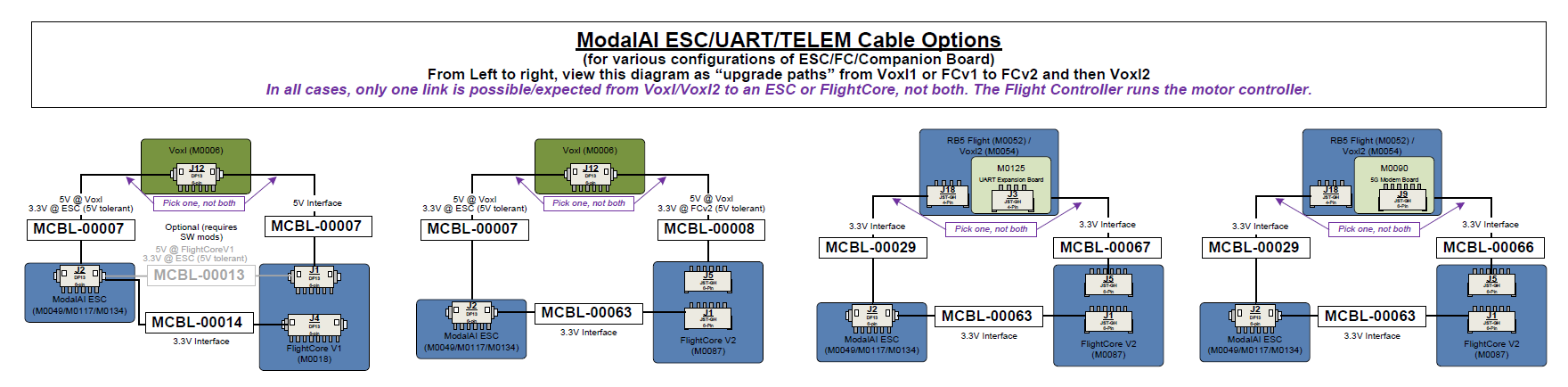
Note: The STM32 has very specific paramters to allow 5V tolerance on UART RX pins. In the diagram above, for FCv2, we meet that constraint. However, if a customer uses a custom config, be sure to check all specs.
Recommended Parts to Order:
Note: Several parts below can be found in kits from Amazon or other large retailers, but they are most commonly knock-offs. Be sure your parts are genuine or you may have some issues following these guides and experience reliability problems long-term.
- 6-position JST GH Shrouds, Digikey Link Here
- 4-position JST GH Shrouds, Digikey Link Here
- Pre-crimped JST GH Pin Contact (SSHL-002T-P0.2) Jumper cable (gives you two contacts per cable, ideal for splicing, can also get in shorter lengths), Digikey Link Here
Tips for making cables:
Get a good set of ESD safe tweezers.
Use a well-lit area with a magnifying glass (helps you find the very small pin 1 arrows or notches).
Plan to discard the old plastic shrouds/housing when re-pinning connectors:
- When taking an existing JST/Hirose/0.025” pin header pin from a shroud, it is important to salvage the pin contact and the integrity of the “barb” that latches into the plastic housing. Therefore, we recommend using tweezers and flipping up the plastic tab that the barb grabs onto, and deliberately damage the plastic shroud that is being replaced anyway. If you press into the crimp terminal to push the barb down, it is required to then pry it back up, which adds a micro-fracture and stress crack into the metal crimp terminal. Crimp tools are expensive (so buy the pre-crimped wires posted above) and soldering is annoying and can be unreliable. Therefore, just toss your old plastic housing when you re-pin anything. Doing this will ensure the maximum integrity of the crimp terminal and wire connection to the housing.
Cables that work the same as FCv1:
MCBL-00004 PWM Output Cable
MCBL-00005 RC Input Cable (Spektrum)
MCBL-00008 VOXL to Flight Controller 2W UART TELEM1 port J1 (Dronecode Compliant, can be ESC or MAVLINK, SW Depending)
- Note, Voxl J12 is a 5V bus. FCv1 J1 is also a 5V bus. However, FCv2 J1 port is a 3.3V bus to be in-line with Dronecode, but it is 5V Tolerant due to buffers on J1. All other FCv2 ports are NOT 5V compliant since they are direct to the MCU which has an ABS max of 4.0V on all signal pins. There are a few noted exceptions as shown in the diagram above. Most of the Recieve UART pins are 5V tolerant, but the receive buffers on the other side loose a lot of noise margin. It gets complicated really fast parsing through the MCU datasheet and running PX4 on-top. Always reach out if you need more info.
- The other two 6-pin DF13 ports on Voxl (J10, J11) are 3.3V signal levels, and therfore with MCBL-00008, can connect to FCv2 J1 or J5.
MCBL-00009 4-pin JST to micro USB Female/Receptacle Cable
MCBL-00028-2 Seeker GPS Cable
Cables Already in Process on ModalAI.com, but you can get a jump start if you want:
This tutorial Here is a great step-by-step with detailed photos showing how to make an MCBL-00061 from an MCBL-00015. Once you have reviewed this tutorial, any of the changes shown below should be easy to follow, understand, and replicate as you need!
The format here is showing how to make a new cable from an existing one (Existing -> New) by swapping out a few shrouds and re-pinning them.
MCBL-00003 → MCBL-00062 (Standalone power from APM)
- From MCBL-00003
- Keep Molex Mini-Spox side
- Change JST 6-pin to JST 4-pin GHR-04V-S as follows:
- pin 1 of Molex to pin1 of 4-pin JST, 2:2, 3:3, 4:4
- Power plugs into M0087 J13 (Might be RED)
MCBL-00011 → MCBL-00211 (APM to Voxl/Voxl2 + FCv2)
- From MCBL-00011
- Keep Both Molex Mini-Spox sides
- Change JST 6-pin to JST 4-pin GHR-04V-S as follows:
- pin 1 of Molex to pin1 of 4-pin JST, 2:2, 3:3, 4:4
- Power plugs into M0087 J13 (Might be RED)
FrSKY/S.BUS 5V RC Cables: On FCv1, 3-pin JST for J9 now moves to a 4-pin JST J8 (CANBUS Port) since that is the only “free” +5V source easily picked up
MCBL-00018 → MCBL-00218 ( FCv2 RC Input (S.Bus, FrSky))
- From MCBL-00018
- Keep 3-pin Harwin Socket and 4-pin JST (with the single wire)
- Change 3-pin JST red/black to 4-pin JST GHR-04V-S as follows:
- Pin 1 stays to Pin 1
- Pin 2 and now Pin 3 stay empty on the new 4-pin
- Pin 3 moves to pin 4 (GND)
FrSKY/S.BUS 5V RC Cables: Switching from FCv1 to VOXL2 I/O (M0065) to effectively make MCBL-00064
MCBL-00018 → MCBL-00064 ( FCv2 RC Input (S.Bus, FrSky))
- From MCBL-00018
- Keep 3-pin Harwin Socket and 4-pin JST (with the single wire)
- Keep Pin 1 of Harwin Socket to Pin 3 of 4-pin JST (Signal)
- Remove (and discard) 3-pin JST housing. Red and black cables remap to the 4-pin JST as follows:
- Pin 1 of the 3-pin JST now moves to Pin1 of the 4-pin JST (+5V)
- Pin 3 of the 3-pin JST now moves to Pin4 of the 4-pin JST (GND)
MCBL-00021 → MCBL-00221 ( FCv2 RC Input (FrSky R-XSR))
- From MCBL-00021
- Keep 5-pin Picoblade socket and 4-pin JST (with the single wire)
- Change 3-pin JST red/black to 4-pin JST GHR-04V-S as follows:
- Pin 1 stays to Pin 1
- Pin 2 and now Pin 3 stay empty on the new 4-pin
- Pin 3 moves to pin 4 (GND)
MCBL-00029 → MCBL-00063-1 ( FCv2 to ModalAI ESC, 200mm)
- From MCBL-00029
- Keep the Hirose DF13 side
- Change JST 4-pin to JST 6-pin GHR-06V-S as follows:
- Pin 2 and Pin 3 of 4-pin move to pin 2 & pin 3 of 6-pin.
- Pin 4 GND of 4-pin to pin 6 GND of 6-pin JST
MCBL-00008 → MCBL-00063-2 ( FCv2 to ModalAI ESC, 90mm)
- From MCBL-00008
- Keep the Hirose DF13 side
- Repin the JST 6-pin to swap pins 2&3:
- Pin 2 and Pin 3 of 6-pin JST swap positions in the housing.
- Note, it might be OK to keep this housing if you replace them carefully, otherwise, you should plan on replacing the housing as per our standard reccomendations.
- In the case of housing replacement, be sure to keep Pin 6 in the same Pin 6 location along with the 2 swaps noted above.